 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1164297
中國鈾資源進口分析(2023-2032年)Research Report on China's Uranium Resource Import 2023-2032 |
||||||
近年來,我國核電發展突飛猛進。 到2022年底,中國將有53座商業核電站投入運行,總裝機容量5560萬千瓦。 在建核電站23座,總裝機容量2419萬千瓦。 中國核電在建容量連續多年位居世界第一。 隨著中國核電裝機容量的增加,對中國鈾資源的需求也在增加。 中國鈾資源貧乏,總儲量不足20萬噸,開採成本高,每年必須進口大量鈾資源。
示例視圖
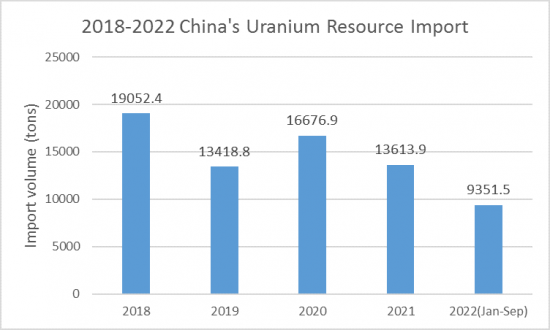
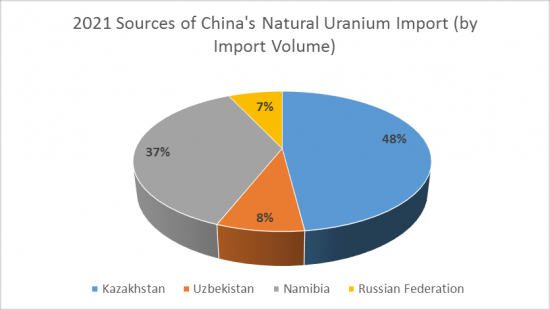
2021年我國將進口鈾資源13613.9噸(同比下降18.4%),進口額13.1億美元(同比下降22.6%)。 2022年前三季度,中國進口鈾9351.5噸(同比增長5.2%),進口額13.6億美元(同比增長48.5%)。
從 2018 年到 2022 年,鈾的平均進口價格將保持波動。 2019年鈾資源進口均價為125.2美元/公斤(同比上漲38.3%),但2019-2021年持續下降,2021年達到96.5美元/公斤。 2022年前三季度,鈾的平均進口價格大幅上漲至145.6美元/公斤,比2021年同期上漲41.1%。
中國進口兩類鈾資源:天然鈾和U235濃縮鈾。 2021年中國將進口天然鈾13535.8噸(佔進口運費的99.4%),進口額12.1億美元(佔進口總額的92.4%)。 2021年中國從5個國家和地區進口天然鈾資源。 按進口量計算,哈薩克斯坦是中國最大的天然鈾進口來源國。 2021年,中國將從哈薩克斯坦進口價值5.5億美元的鈾資源6459.1噸(佔進口總量的47.7%)。
隨著中國核電廠數量的不斷增加以及對鈾資源的需求不斷擴大,預計從 2023 年到 2032 年,中國的鈾進口量將繼續增加。
在本報告中,我們分析了中國鈾資源進口市場,包括總體進口量和進口價值、主要進口來源地(2018-2022 年)、按類型分類的詳細趨勢、進口價格趨勢,我們將匯總並發布主要市場信息驅動因素和製約因素、主要參與者的概況和戰略,以及未來進口趨勢的展望(2023-2032 年)。
內容
第一章中國鈾進口分析(2018-2022)
- 中國鈾資源進口規模
- 中國進口鈾資源
- 中國鈾資源進口值
- 中國鈾進口價格
- 中國鈾資源表觀消費量
- 中國對進口鈾資源的依賴
- 中國主要的鈾資源進口國
- 進口量
- 進口價值
第2章中國天然鈾進口分析(2018-2022)
- 進口量
- 進口價值
- 進口價格
- 依賴進口
- 按類型進行進口分析
- 進口量:按類型分類
- 導入值:按類型
- 進口價格:按類型
- 主要進口商
- 進口量
- 進口價值
第三章中國濃縮鈾進口分析(2018-2022)
第四章中國鈾資源主要進口來源地分析(2018-2022年)
- 哈薩克斯坦鈾資源進口分析
- 從納米比亞進口鈾資源分析
- 從烏茲別克斯坦進口鈾資源分析
- 從俄羅斯進口鈾資源分析
- 從德國進口鈾資源分析
- 從其他國家進口鈾資源的分析
第5章中國鈾進口展望(2023-2032)
- 影響中國鈾資源進口的因素
- 有利因素
- 不利因素
- 中國鈾進口預測 (2023-2032)
- 進口量預測
- 進口量預測:按主要進口來源
- 進口量預測:按主要類型
In recent years, China has seen rapid development of nuclear power. By the end of 2022, China had 53 commercial nuclear power units in operation, with a total installed capacity of 55.6 million kilowatts. There are 23 nuclear power units under construction, with a total installed capacity of 24.19 million kilowatts. China's installed capacity of nuclear power generation units under construction has remained the world's largest for many years. As China's installed nuclear power capacity rises, so does the country's demand for uranium resources. Since China's indigenous uranium resources are poor, with total reserves of no more than 200,000 tons and high mining costs, China needs to import large amounts of uranium resources every year.
SAMPLE VIEW


In 2021, China's imports of uranium resources reached 13,613.9 tons, down 18.4% year-on-year, and the import value of US$1.31 billion, down 22.6% year-on-year. In the first three quarters of 2022, China imported 9,351.5 tons of uranium, up 5.2% year-on-year, and US$1.36 billion in imports, up 48.5% year-on-year, according to CRI analysis.
The average import price of uranium is volatile in 2018-2022. In 2019, the average import price of uranium resources in China is US$125.2 per kg, an increase of 38.3% year-on-year. According to CRI's analysis, the average import price of uranium decreases continuously from 2019 to 2021, with the average import price of uranium decreasing to US$96.5 per kg in 2021. In the first three quarters of 2022, the average import price of uranium increases significantly to US$145.6 per kg, an increase of 41.1% compared to the same period in 2021.
China imports uranium resources mainly in two categories: natural uranium and U235 enriched uranium. In 2021, China imported 13,535.8 tons of natural uranium, accounting for 99.4% of total imports, and the import value of US$1.21 billion, accounting for 92.4% of total imports. In 2021, China imported natural uranium resources from five countries and regions. According to CRI's analysis, Kazakhstan is the largest source of natural uranium imports to China by import volume. In 2021, China imported 6,459.1 tons of natural uranium from Kazakhstan, accounting for 47.7% of total natural uranium imports, and US$550 million, or 45.6% of total natural uranium imports.
China lacks indigenous uranium resources and is highly dependent on imports. China's nuclear power generation accounts for approximately 5% of the country's total power generation, leaving much room for improvement, and CRI expects that China's uranium imports are expected to continue to rise from 2023-2032 as the country's installed nuclear power generation rises further and demand for uranium resources continues to grow.
Topics covered:
- China's Uranium Resource Import Status and Major Sources in 2018-2022
- What is the Impact of COVID-19 on China's Uranium Resource Import?
- Which Companies are the Major Players in China's Uranium Resource Import Market and What are their Competitive Benchmarks?
- Key Drivers and Market Opportunities in China's Uranium Resource Import
- What are the Key Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities for China's Uranium Resource Import during 2023-2032?
- What is the Expected Revenue of China's Uranium Resource Import during 2023-2032?
- What are the Strategies Adopted by the Key Players in the Market to Increase Their Market Share in the Industry?
- What are the Competitive Advantages of the Major Players in China's Uranium Resource Import Market?
- Which Segment of China's Uranium Resource Import is Expected to Dominate the Market in 2032?
- What are the Major Adverse Factors Facing China's Uranium Resource Import?
Table of Contents
1. 2018-2022 China Uranium Resources Import Analysis
- 1.1. Import Scale of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.1. Import Volume of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.2. Import Value of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.3. Import Price of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.4. Apparent Consumption of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.5. Import Dependence of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.2 Major Import Sources of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.2.1. By Import Volume
- 1.2.2. By Import Value
2. China's Natural Uranium Import Analysis, 2018-2022
- 2.1 Natural Uranium Import Volume
- 2.2 Natural Uranium Import Volume
- 2.3. Natural Uranium Import Prices
- 2.4 Import Dependence of Natural Uranium
- 2.5 Import Analysis of Natural Uranium by Type
- 2.5.1 Natural Uranium Imports by Type
- 2.5.2 Import Value of Natural Uranium by Category
- 2.5.3. Import Prices of Natural Uranium by Category
- 2.6 Sources of Natural Uranium Imports
- 2.6.1. By Import Volume
- 2.6.2. By Import Value
3. 2018-2022 China Import Analysis of Enriched Uranium
- 3.1. Import Volume of Enriched Uranium
- 3.2. Import Value of Enriched Uranium
- 3.3. Import Price of Enriched Uranium
- 3.4 Import Dependence of Enriched Uranium
- 3.5 Analysis of Various Types of Enriched Uranium Imports
- 3.5.1 Enriched Uranium Imports by Type
- 3.5.2. Import Value of Enriched Uranium by Type
- 3.5.3. Import Prices of Various Types of Enriched Uranium
- 3.6 Import Sources of Enriched Uranium
- 3.6.1. By Import Volume
- 3.6.2. By Import Value
4. 2018-2022 Analysis of Major Import Sources of Uranium Resources in China
- 4.1 Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from Kazakhstan
- 4.2. Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from Namibia
- 4.3 Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from Uzbekistan
- 4.4 Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from the Russian Federation
- 4.5 Analysis of Uranium Imports into Germany
- 4.6 Analysis of Other Uranium Resources Imports
5. China's Uranium Resource Import Outlook 2023-2032
- 5.1 Factors Affecting China's Uranium Resource Imports
- 5.1.1 Favorable Factors
- 5.1.2 Disadvantageous Factors
- 5.2. China's Uranium Resource Import Forecast, 2023-2032
- 5.2.1 Import Volume Forecast
- 5.2.2. Forecast of Major Import Sources
- 5.2.3. Forecast of Major Imported Uranium Resources Types








