 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1430583
日本貨運與物流:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2024-2029)Japan Freight and Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
價格
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
簡介目錄
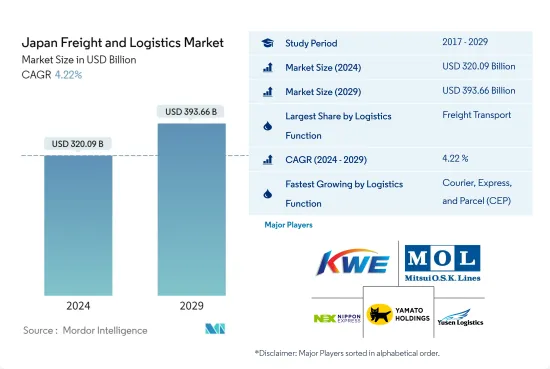
日本貨運和物流市場規模預計2024年為3,200.9億美元,預計2029年將達到3,936.6億美元,預測期內(2024-2029年)年複合成長率為4.22%,預計將持續成長。

由於日本電子商務銷售增加和結構變化,公路貨運服務需要增加
- 全球貨物和材料出口和進口的快速成長預計將在預測期內推動日本公路貨運市場。日本的道路貨運業正在經歷快速發展和結構變革,以滿足不斷成長的需求。 90%以上的貨運公司是中小企業。由於電子商務網站的需求不斷成長,用於貨運的輕型汽車和貨車的數量預計將很快增加。儘管現金收入不斷增加,勞動人口不斷成長,但由於司機迅速老化,維持電子商務和整個低成本國內市場所需的勞動力正在減少,供應仍然受到威脅。
- 日本的電商航運業格局由三大擴張組織主導,控制國內90%以上的宅配市場。最大的承運商 Yamato Transport 每年運送超過 18 億個包裹。拮抗佐川急便為包括亞馬遜在內的主要客戶提供物流服務。日本郵政排名第三。
- 2019會計年度,公共道路建設維護投資約617.1億美元,高於上年度的563億美元。建設成本超過維護成本超過 119.2 億美元。據國土交通省稱,為了應對老化,到2044會計年度左右,國土交通省每年的公共基礎設施支出預計將比2018會計年度增加約40%基礎設施。

日本貨運和物流市場的趨勢
由於宅配的需求不斷成長和勞動力短缺,MILT 正在重點建造自動化貨運道路和物流隧道。
- 報告期間內,交通運輸和倉儲業佔GDP的比重較大。截至2022年,建設投資總額將達到68.8兆日圓(5,216.3億美元),仍是東南亞基礎建設投資最多的國家。此外,2023年10月,國土交通省宣布了一項以開發自動化貨運專用道路為中心的臨時計畫。由於宅配的需求不斷成長和勞動力短缺,該國還計劃創建一個系統,讓自動駕駛汽車穿過專用物流的地下隧道。
- 日本運輸和倉儲業呈現顯著成長,從2021年年與前一年同期比較0.57%成長到2022年年增4.94%。這主要得益於運輸和物流領域的技術創新以及對自動化、人工智慧和機器人的投資,提高了物流業務效率、降低了成本並提高了服務品質。日本由於其龐大的製造業以及對高效貨物儲存和發行的需求,嚴重依賴強大的物流業。 2021年,日本國內貨物吞吐量約47.1億噸,外貿貨物吞吐量將再增加9億噸。
- 2021年,包括積體電路及相關半導體產品與前一年同期比較的數位商品貿易額將達4.34兆美元,較去年同期成長21.3%。電腦及周邊設備等電氣和電子產品的貿易也推動了成長。

日本政府將汽油補貼制度延長至年終,擔心如果補貼制度終止,汽油價格將會上漲。
- 截至2021年12月,日本柴油月平均零售價約為每公升1.06美元,低於2020年12月的0.95美元。 2022年第一季柴油平均價格為1.07美元,最低價為2022年5月1.04美元,最高價為2022年6月1.09美元。相比之下,這段時期的全球平均柴油價格為每公升1.93美元。
- 過去幾個月油價上漲引發了人們對通膨上升的擔憂,並引發了全球經濟的不確定性。日本已要求生產國增加產量,並於2022年1月啟動臨時補貼制度。此後價格加倍,達到每公升 50 日圓(0.37 美元)的上限。受全球原油價格飆升的影響,日本平均零售汽油價格在2022年達到了過去七年來的最高水準。 2022年第二季普通汽油平均價格為每公升1.4美元,為2014年10月以來的最高水平,較2021年10月上漲25美分(0.25美元)。
- 由於通膨上升和全球經濟不確定性,預計汽油和原油價格將保持高位,進而影響零售價格。由於日圓疲軟和政府補貼逐漸減少,日本各地的普通汽油價格創下歷史新高。 2022 年全國加油站的平均汽油價格為每公升 185.6 日圓(1.27 美元)。從2023年6月開始,政府逐步降低了已達到30%的補貼率,並在9月底石油市場穩定後結束了該計畫。日本將汽油補貼計畫延長至年終,以應對補貼計畫結束後汽油價格上漲的擔憂。

日本貨運物流業概況
日本貨運物流市場較分散,前五名企業比例為11.49%。該市場的主要企業是(按字母順序排列)近鐵通運、商船三井、日本通運、大和控股和郵船物流。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章執行摘要和主要發現
第2章 檢舉要約
第3章簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
- 調查方法
第4章 產業主要趨勢
- 人口統計
- 按經濟活動分類的 GDP 分佈
- 按經濟活動分類的 GDP 成長率
- 通貨膨脹率
- 經濟表現和概況
- 電商產業趨勢
- 製造業趨勢
- 交通運輸倉儲業GDP
- 出口趨勢
- 進口趨勢
- 燃油價格
- 卡車運輸成本
- 按類型分類持有的卡車數量
- 物流成果
- 主要卡車供應商
- 模態佔有率
- 海運能力
- 班輪連接
- 停靠港和表演
- 貨運趨勢
- 貨物噸位趨勢
- 基礎設施
- 法律規範(公路和鐵路)
- 日本
- 法律規範(海事/航空)
- 日本
- 價值鍊和通路分析
第5章市場區隔(1.所有細分市場的市場區隔,2.貨運、CEP(快遞、快遞、小包裹)和倉庫/倉儲等特定細分市場的市場規模;3.到2029年的預測和成長前景分析)
- 最終用戶產業
- 農業、漁業、林業
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 石油和天然氣、採礦和採石業
- 批發零售
- 其他
- 物流功能
- 快遞、快遞、小包裹(CEP)
- 目的地
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 貨物運輸
- 按運輸方式
- 航空
- 海上/內河供水
- 其他
- 貨物運輸
- 透過交通工具
- 航空
- 管道
- 鐵路
- 路
- 海上/內河航道
- 倉儲
- 溫度控制
- 非溫控
- 溫度控制
- 其他服務
- 快遞、快遞、小包裹(CEP)
第6章 競爭形勢
- 主要策略趨勢
- 市場佔有率分析
- 公司形勢
- 公司概況(包括全球概況、市場層級、主要業務部門、財務狀況、員工人數、關鍵資訊、市場排名、市場佔有率、產品和服務、最新動態的分析)。
- DB Schenker
- Deutsche Post DHL Group
- DSV A/S(De Sammensluttede Vognmand af Air and Sea)
- Hanjin Shipping
- Kintetsu World Express
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Mitsui OSK Lines, Ltd.
- Nippon Express
- United Parcel Service
- Yamato Holdings Co. Ltd
- Yusen Logistics
第7章 CEO 面臨的關鍵策略問題
第8章附錄
- 世界概況
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 世界價值鏈分析
- 市場動態(市場促進因素、限制因素、機會)
- 技術進步
- 資訊來源和參考文獻
- 圖表清單
- 重要見解
- 資料包
- 詞彙表
- 外匯
簡介目錄
Product Code: 66498
The Japan Freight and Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 320.09 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 393.66 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.22% during the forecast period (2024-2029).


Rising demand for road freight services witnessed owing to increasing ecommerce sales and structural changes in Japan
- The surge in imports and exports of goods and materials worldwide is expected to drive the Japanese road freight transport market during the forecast period. Japan's road freight industry is undergoing rapid development and structural changes to meet the growing demand. Over 90% of truck carriers are small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Because of the growing demand for e-commerce sites, the number of mini cars and vans used for cargo transportation is expected to increase soon. Despite increasing cash income and a growing labor force, as drivers age rapidly, the supply of labor needed to maintain e-commerce and the overall low-price domestic market is still under threat.
- Japan's e-commerce transportation industry pattern is dominated by three expansion organizations, which control more than 90% of the domestic parcel delivery market. The largest transporter, Yamato Transport Company, delivers more than 1.8 billion packages each year. Close competitor Sagawa Express provides logistics services to major customers, including Amazon. Japan Post is the third-largest player.
- In FY 2019, investments in public roads for construction and maintenance amounted to approximately USD 61.71 billion, up from USD 56.3 billion in the previous fiscal year. Construction expenditures exceeded maintenance costs by more than USD 11.92 billion. According to the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT), only the Ministry's yearly expenditures on public infrastructure are expected to increase by roughly 40% until around FY 2044 compared to 2018 to counter infrastructure deterioration.

Japan Freight and Logistics Market Trends
With growing demand for home deliveries & labour shortages, the MILT is focusing on construction of automatic cargo transport roads and logistics tunnels
- The transportation and storage sector has captured a significant percentage of GDP over the review period. The country still leads in Southeast Asian infrastructure investment with total construction investment reaching JPY 68.8 trillion (USD 521.63 billion) as of 2022. Moreover, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MILT) published an interim draft in October 2023, with a focus on developing a dedicated road for automatic cargo transportation. Owing to rising home delivery demands and labour shortages, the country is further aiming to build a system where self-driving carts run through underground tunnels dedicated to logistics.
- The transportation and storage sector in Japan saw a significant increase, rising from 0.57% YoY growth in 2021 to 4.94% YoY in 2022. This was primarily due to technological innovations in transportation and logistics and investments in automation, artificial intelligence, and robotics, which enhanced the efficiency of logistics operations, reducing costs and improving service quality. Japan relies heavily on a robust logistics industry, driven by its sizable manufacturing sector and the resulting need for efficient goods storage and distribution-consequently, shipping firms like Yamato Holdings rank among the world's top logistics companies. In 2021, Japan handled approximately 4.71 billion tons of domestic freight and an additional 900 million tons of cargo through foreign trade.
- In 2021, the trade in digital commodities, including integrated circuits and related semiconductor items, experienced a notable 21.3% increase compared to the previous year, reaching a substantial value of USD 4.34 trillion. The trade of electrical and electronic goods like computers and peripheral equipment also drove the growth.

Japan's government extended the gasoline subsidy program till 2023 year-end in response to concerns that gasoline prices will rise if the subsidy program is terminated
- As of December 2021, the monthly average domestic retail price of diesel fuel in Japan stood at around USD 1.06 per liter, a decrease from USD 0.95 in December 2020. The average diesel price during the Q1 of 2022 was USD 1.07, with a minimum of USD 1.04 in May 2022 and a maximum of USD 1.09 in June 2022. In comparison, the average price of diesel in the world for this period was USD 1.93 per liter.
- The surge in crude oil prices over the past few months raised concerns regarding increasing inflation and stirred uncertainty in the global economy. Japan requested producer nations to increase their output and launched a temporary subsidy program in January 2022. It has since raised twice the amount to hit a cap of JPY 50 (USD 0.37) per liter. Japan's average retail gasoline price reached its highest level in seven years in 2022, reflecting a global surge in crude oil prices. The average price for regular gasoline was USD 1.4 per liter in Q2 2022, reaching its highest level since October 2014 and indicating an increase of 25 cents (USD 0.25) from October 2021.
- Gasoline and crude oil prices are expected to remain high and influence retail prices due to increasing inflation and economic uncertainty globally. A weak Yen and a gradual reduction in government subsidies have led to record-high prices of regular gasoline across Japan. The average gasoline price at the nation's gasoline stands was JPY 185.6 (USD 1.27) per liter in 2022. Since June 2023, the government has gradually reduced the subsidy rate, which stands at 30%, to terminate the program at the end of September, as the crude oil market has regained calm. Japan extended the year-end gasoline subsidy program in response to concerns that gasoline prices will rise if the subsidy program is terminated.

Japan Freight and Logistics Industry Overview
The Japan Freight and Logistics Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 11.49%. The major players in this market are Kintetsu World Express, Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd., Nippon Express, Yamato Holdings Co. Ltd and Yusen Logistics (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.11 Trucking Fleet Size By Type
- 4.12 Logistics Performance
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Modal Share
- 4.15 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.16 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.17 Port Calls And Performance
- 4.18 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.19 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.20 Infrastructure
- 4.21 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.21.1 Japan
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.22.1 Japan
- 4.23 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes 1. Market value in USD for all segments 2. Market volume for select segments viz. freight transport, CEP (courier, express, and parcel) and warehousing & storage 3.Forecasts up to 2029 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 DB Schenker
- 6.4.2 Deutsche Post DHL Group
- 6.4.3 DSV A/S (De Sammensluttede Vognmand af Air and Sea)
- 6.4.4 Hanjin Shipping
- 6.4.5 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.4.6 Kuehne + Nagel
- 6.4.7 Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Nippon Express
- 6.4.9 United Parcel Service
- 6.4.10 Yamato Holdings Co. Ltd
- 6.4.11 Yusen Logistics
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FREIGHT AND LOGISTICS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (Market Drivers, Restraints & Opportunities)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
- 8.7 Currency Exchange Rate
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219










