 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1435880
日本低溫運輸物流:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2024-2029)Japan Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
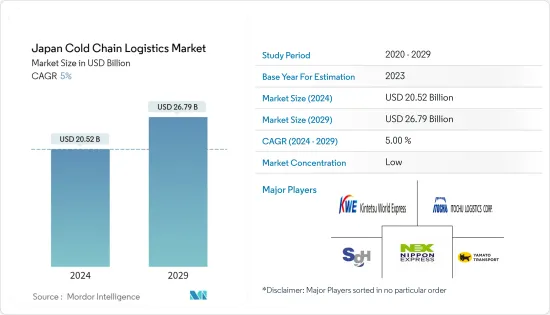
日本低溫運輸物流市場規模預估2024年為205.2億美元,預估至2029年將達267.9億美元,在預測期間(2024-2029年)成長5%,年複合成長率為%。
由於COVID-19的影響,日本貿易省報告稱,2020年3月藥妝店銷售額與前一年同期比較成長了7.5%。與此一致,日本超級市場協會宣布,為了因應自我隔離和自行做飯的需求,2020年3月超級市場食品的需求和銷售量與前一年同期比較增加了7.4%。這些因素都對日本低溫運輸物流市場產生了負面影響。 COVID-19 影響了日本的低溫運輸業務,包括日益增加的食品安全問題。
日本被認為是成熟的低溫運輸物流市場,由多家參與者主導。由於生物製藥和再生醫學的快速發展,日本對冷藥品連鎖店的需求最近有所增加。隨著 COVID-19感染疾病和其他治療方法的推出,這一趨勢預計將持續下去。日本的低溫運輸物流最初是針對生鮮食品、冷藏食品、冷凍食品產業而建立的。低溫運輸物流的重點是在持續控制的溫度和濕度環境下及時交付產品。
日本的冷庫設施大部分由大型低溫運輸公司擁有和經營,只有少量設施可供租賃。隨著冷凍冷藏產品電商使用的增加,有潛在需求的地區冷庫建設將加快。
冷庫數量的增加和製藥業的成長等因素預計將推動日本低溫運輸物流市場的成長。市場面臨的挑戰包括冷庫容量分配不規範、缺乏足夠的物流連接支援以及需要大量的資本投資。
日本低溫運輸物流市場趨勢
現代家庭引發對冷凍食品的需求
隨著老年人的獨立、雙收入家庭和單身人數的增加、食品浪費危機以及食品人手不足現代家庭的解決方案,冷藏和冷凍食品的需求不斷增加食品整個食品工業。飲料業。
日本生產的熱門冷凍食品包括餃子(gyoza)、炸丸子和麵條(烏龍麵)。近年來,日本食品尤其是農產品在世界各地爆普及。
在人口老化的日本,向健康的預期壽命過渡是支持冷凍食品銷售的人們的通用。超級市場、超級市場、藥局也大幅成長。由於冷凍技術的進步以及新冠病毒 (COVID-19 ) 的感染疾病導致對家常飯菜的需求增加,日本的冷凍食品已經多樣化。
來自名店的昂貴美食和來自海外的正宗複製品已經蔓延到市場,百貨公司和超市也加快了擴大銷售範圍的步伐。
日本製藥業的成長
日本是世界上最大的醫藥市場之一,這主要是由於其人口老化。在政府積極推廣學名藥的支持下,該公司也是先進醫療設施的領先製造商和進口商之一。
該國的本土生技藥品產業僅次於美國。再加上政府對支持低成本仿冒品的重視,這為生物相似藥提供了巨大的機會。創新製藥公司長期以來一直受益於日本慷慨的獨佔期,但該國在學名藥普及方面正在追趕其他成熟市場。
對這一體系的信心體現在國內製藥公司擴大將其產品分銷到全球的事實中。日本企業的海外銷售佔有率穩定上升,對低溫運輸儲運設施的需求也增加。引起人們對日本製藥業興趣的另一個重要因素是需要加強日本的藥物發現生態系統。
該國 COVID-19感染疾病人數的增加增加了對處方藥和疫苗的需求。它影響了藥品的需求。由於 COVID-19感染疾病進口增加,藥品需求增加。例如,2021年5月,日本政府與輝瑞-BioNTech簽署協議,在年終進口1.94億劑(133萬美元)疫苗。根據 IQVIA 的數據,2021 年日本處方藥市值約為 10.6 兆日圓(800 億美元),高於 2020 年的約 10.4 兆日圓(790 億美元)。
日本低溫運輸物流產業概況
市場相對分散,國內外參與者眾多,包括日本通運、雅瑪多運輸、佐川急便、伊藤忠物流株式會社和近鐵世界通運。市場競爭與成本、倉儲費、空間以及包裝和包裝材料價格的上漲有關。服務供應商繼續致力於開發提供流程標準化的功能。缺乏與儲存溫度和操作程序相關的標準化是該行業面臨的進一步重大挑戰。可用冷庫空間的品質和彈性是一個主要問題。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月分析師支持
目錄
第1章簡介
- 研究成果
- 調查先決條件
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章市場動態與洞察
- 目前的市場狀況
- 市場動態
- 促進因素
- 醫療保健產業的重要性
- 消費者對生鮮食品的需求增加
- 抑制因素
- 如果包裝不充分或產品損壞
- 溫控混亂
- 機會
- 創新
- 促進因素
- 技術趨勢和自動化
- 政府法規和舉措
- 產業價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 專注環境溫度/溫控存儲
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代產品的威脅
- 競爭公司之間的敵意強度
- 排放標準法規對低溫運輸產業的影響
- 新型冠狀病毒感染疾病(COVID-19)對市場的影響
第5章市場區隔
- 按服務
- 貯存
- 交通設施
- 附加價值服務(冷凍、標籤、庫存管理等)
- 按溫度類型
- 冷藏
- 冷凍的
- 按用途
- 園藝(新鮮水果和蔬菜)
- 乳製品(牛奶、冰淇淋、奶油等)
- 肉、魚、家禽
- 加工過的食品
- 製藥、生命科學、化學
- 其他用途
第6章 競爭形勢
- 市場集中度概況
- 公司簡介
- Nippon Express
- Yamato Holdings
- Sagawa
- Kintetsu World Express
- Itochu Logistics Corp.
- DHL
- Kuehne Nagel
- K line Logistics
- Nichirei Logistics Group, Inc.
- Sojitz Corporation
- CEVA Logistics
- Kokubu Goup
- Agility
- SF Express*
第7章 日本低溫運輸物流市場的未來
第8章附錄
The Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 20.52 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 26.79 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

With COVID-19 in effect, the Japanese Trade Ministry reported a 7.5% Y-o-Y increase in the sale of drugstores in March 2020. Along with this, the Japan Supermarkets Association, in response to the self-imposed quarantines and the need to cook at home, reflected a 7.4% Y-o-Y increase in the demand and sales of groceries at the supermarkets in March 2020. All these factors led to a negative impact on the cold chain logistics market in Japan. COVID-19 impacted Japan's cold chain operations, including increased food safety concerns.
Japan is regarded as a mature market for cold chain logistics and is dominated by several players. Rapid advancements in biopharmaceuticals and regenerative medicine recently increased the demand for the cold pharmaceutical chain in Japan. This trend is expected to continue with the COVID-19 vaccines introduction and other treatments. Cold chain logistics in Japan was initially established for the fresh, refrigerated, and frozen food industries. Cold chain logistics focuses on the timely distribution of products within a constantly controlled temperature and humidity environment.
Most cold storage facilities in Japan are owned and operated by major cold chain corporations, with only a small number available for lease. Advances in using e-commerce to sell frozen and chilled goods will accelerate cold storage development in areas with latent needs.
Factors such as an increase in the number of refrigerated warehouses and growth in the pharmaceutical sector are expected to drive the growth of Japan's cold chain logistics market. Some of the challenges in the market are the irregular distribution of cold storage capacity, lack of proper logistical connectivity support, and the need for high capital investment.
Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market Trends
Modern Households Leading to Demand for Frozen Foods
The demand for chilled/frozen foods is increasing as a solution for modern-age families, such as independent elderly citizens, increase in dual-income households and single people, along with the danger of food loss and increasing overall labor shortages in the food and beverage industry.
In 2021, the consumption volume of frozen food in Japan amounted to about 2.9 million tons (USD 0.020 million tons). Popular frozen food products manufactured in Japan include dumplings (gyoza), croquettes, and wheat-flour noodles (udon). In recent years, Japanese food also exploded worldwide, especially agricultural products.
As the Japanese population ages, the shift to healthy life expectancy is a common desire of the people aiding the sale of frozen products. It also significantly increased in supermarkets, hypermarkets, and drugstores. Frozen food items in Japan became more diverse due to advances in refrigeration technology and growing demand for eat-at-home products amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
High-priced delicacies from well-known restaurants and authentic reproductions of food from abroad grew across the market, prompting department stores and supermarkets to speed up efforts to expand sales spaces.
Growth of Pharmaceutical Sector in Japan
Japan is one of the largest pharmaceutical markets in the world, primarily due to its aging population. It is also among the major producers and importers of advanced medical facilities backed by active government initiatives to promote generic drugs.
The country's native biologics sector is second after the USA. Coupled with the government's focus on supporting lower-cost copycat products, this entails a massive opportunity for bio-similars. While innovative drugmakers long benefited from generous exclusivity periods in Japan, the country is catching up with other mature markets regarding generics penetration.
The confidence in the system is reflected by the fact that domestic drugmakers are increasingly going global with their products. With the share of top Japanese companies' overseas sales rising steadily, the demand for cold chain storage and transportation facilities is also increasing. Another critical factor for increased interest in Japan's pharmaceuticals sector is the need to enhance Japan's drug discovery ecosystem.
The increased COVID-19 infection cases in the country increased the demand for prescription drugs and vaccines. It impacted the pharmaceutical product demand. The increasing import of COVID-19 vaccines increased the pharmaceutical product demand. For instance, in May 2021, the Japanese government signed a contract with Pfizer-BioNTech to import 194 million (USD 1.33 million)vaccine doses by the end of 2021. In 2021, the Japanese prescription drug market was valued at approximately JPY 10.6 trillion (USD 0.080 Trillion), up from about JPY 10.4 trillion (USD 0.079 Trillion) in 2020, according to IQVIA.
Japan Cold Chain Logistics Industry Overview
The market is relatively fragmented, with many local and international players, including Nippon Express, Yamato, Sagawa Express Co., Ltd, Itochu Logistics Corp., and Kintetsu World Express. The competition in the market pertains to costs, storage fees, and space, along with the rising prices of packing and packaging materials. The service providers are still working on developing the ability to provide standardization in the processes. Lack of standardization related to storage temperature and operating procedures are a few more significant challenges the industry faces. The quality and flexibility of available cold warehousing space are a considerable concern.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Criticality of the healthcare sector
- 4.2.1.2 Increased consumer demand for fresh foods
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Inadequate packaging or damaged products
- 4.2.2.2 Disrupted temperature control
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Technological Innovations
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Technological Trends and Automation
- 4.4 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.5 Industry Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Spotlight on Ambient/Temperature-controlled Storage
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Emission Standards and Regulations on Cold Chain Industry
- 4.9 Impact of COVID - 19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Services
- 5.1.1 Storage
- 5.1.2 Transportation
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services (Blast Freezing, Labeling, Inventory Management, etc.)
- 5.2 By Temperature Type
- 5.2.1 Chilled
- 5.2.2 Frozen
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Horticulture (Fresh Fruits & Vegetables)
- 5.3.2 Dairy Products (Milk, Ice-cream, Butter, etc.)
- 5.3.3 Meats, Fish, Poultry
- 5.3.4 Processed Food Products
- 5.3.5 Pharma, Life Sciences, and Chemicals
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Nippon Express
- 6.2.2 Yamato Holdings
- 6.2.3 Sagawa
- 6.2.4 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.2.5 Itochu Logistics Corp.
- 6.2.6 DHL
- 6.2.7 Kuehne Nagel
- 6.2.8 K line Logistics
- 6.2.9 Nichirei Logistics Group, Inc.
- 6.2.10 Sojitz Corporation
- 6.2.11 CEVA Logistics
- 6.2.12 Kokubu Goup
- 6.2.13 Agility
- 6.2.14 SF Express*













